HAZOP/HAZID
A good team for HAZOP: a responsible person for operation, process engineer, a chemist with a knowledge of materials and reactions, a moderator who poses good questions. Sometimes, a chemist can not predict the reations, which have to be conveyed adiabatically in the labratory.
Every 5 years, HAZOP and HAZID should be updated.
HAZID/Risk Analysis/ Management of Hazardous Fluids (CAF/CAO): stands for hazard identification/a general risk analysis to alert management
The system is devided into nodes:
- Nodes
- Parameters: Pressure
- Deviations: High
- Consequences: Explosion
- Safeguards: Alarm (If the problem is not very serious)
- Recommendations: …
SIMOPS (Simultaneous Operation Procedure): steps taken during construction, commissioning, start up and operation
HAZOP: for hazard and operability study/ deals with comprehensive and complex workplace operations/ to identify hazards and assess safeguards followed by LOPA (Layer of Protection Analysis),
If additional protection layer is necessary, SIF (Safety Instrumented Function) is applied to achieve SIL (Safety Integrity Level, danger for life with cost damages) or AIL (Asset Integrity Level, only cost damages) for risk reduction
With LOPA, the SIL results from the required reduction in the probability of occurrence. If this has to be reduced by a factor of 10, SIL 1 is sufficient, if a factor of 100 is SIL 2, if a factor of 100 is SIL 3…
we can not change the consequence but only the frequency through SIFs…
Two-man rule (4-Augen Prinzip): control mechanism to achieve a high level of security.
Ignition temperature (Zündtemperatur): The ignition temperature of a substance is the least temperature at which the substance starts combustion. At the ignition temperature, a large fraction of the reactant molecules have more thermal energy than the activation energy.
Activation energy: the minimum quantity of energy which the reacting species must possess in order to undergo a specified reaction.
Flash point (Flammenpunkt): the flash point of a volatile material is the lowest temperature at which its vapors ignite if given an ignition source.
Hydrocarbons are not allowed to be drained into open slop system with high temperature. It results in combustion.
Explosion Types:
- Deflagration: combustion through a gas or across the surface at a subsonic speed driven by heat
- Detonation: combustion through a supersonic shock wave in a body of material
Löschwasserrückhaltebehälter: to collect contaminated löschwasser after any explosion and prevent the contamination of other pipelines.
Fire Class:
A fire class is a system of categorising fire with regard to the type of material and fuel for combustion:

Fire Detection System:
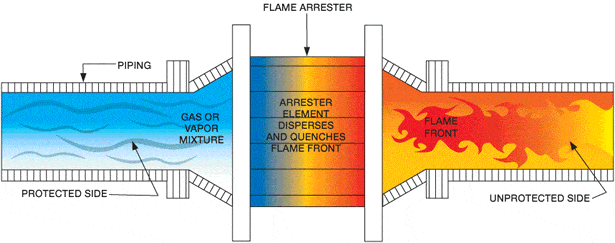
- Flame arrestors (Flammensperre):
- contains inflammable gas or steam-air mixture
- allo flow but prevent flame
2. Protego flame arrestor: having several metal plates with gaps

- prevent flame transmission through narrow gap : gap with(Spaltweite) is a key parameter for the design depending highly on temperature and pressure
- prevent flame to go back to fuel gas network
3. Flame detector:
- Optical for detecting different flammes based on wavelengths
- Ionized for detecting only one flame
4. Passive Fire Protection (PFP)
PSVs:
Every PSV has a spare in warehouse
Car sealed/locked: To seal valves in the open/closed positions with a plastic or metal seal or with a lock
It is highly recommended to keep a large distance between dangerous units having flammable gas to prevent other units from fire.
- Pressure Safety Valve: the opening is sudden
- Directly actuated valves: weight or spring-loaded valves that open at a predetermined pressure, and that normally close after the pressure has been relieved. The system pressure provides the motive power to operate the valve.
- Indirectly actuated: pneumatically- or electrically-operated valves that are activated by pressure-sensing instruments. It relates to the safety instruments not valves.
2. Blow Down Valve: the opening is sudden
3. Pressure Relief Valve: A conventional pressure relief valve is not used when the built-up backpressure is greater than 10% of the set pressure at 10% overpressure.
- Spring-loaded Relief valve: It operates automatically. It is normally closed. If the pressure will be high, the valve will be opened.

- Weighted Relief Valve: It is better than spring loaded valve, since the spring constant is dependant on the temperature. But, the weighted valve is not dependant on it.
Force= Sitzfläche des Ventils *Druck
- Pilot-operated relief valve: It may be pneumatic for gas cases and hydraulic for fluids.
4. Non reclosing Pressure Relief Devices
- Bursting disc
- Breaking-pin devices
Having a working pressure near the set pressure:
If the set point will be often achieved in the plant, the sealings will be damaged.
The pilot-operated relief valve is mostly recommended
The non reclosing valves can be used for having a pressure near the set pressure, while the reclosing relief devices are more sensible to the set point. The non reclosing valve is just gut for once.
Design of safety valves:
The more common causes of overpressure are
- External fire (The most common problem)
- Heat Exchanger
- Tube Failure
- Liquid Expansion (The most common problem)
- Cooling Water Failure
- Electricity Failure
- Blocked Outlet
- Failure of Automatic Controls
- Loss of Reflux
- Chemical Reaction
Procedure:
- Scenarios (resasons of pressure increase in a vessel: mechanical, thermal and chemical reason)
- Data collection
- Phase identification
- Design of valve with this application: https://cse-engineering.de/leistungen/digital-engineering/cse-prosar
- Design of outlet line
- Safe location of outline line (atmosphere or …)
- Documentation
Design according to API521 for Scenarios and API520 for the valve:
- Mass flow rate: due to change of density, the maximum permissible flow rate should considered for the calculation. The mass flow rate depends on the surface area and Kv value ,which can be calculated from scenarios API521, chapter 4, Closed Outlets, Cooling-water failure, Top-tower reflux failure, Abnormal process heat or vapor input, Check valve failure, ..
- Maximum allowable working pressure, which can be higher than design pressure, would be considered as the set pressure. Translation result. If you want to drive 200km/h then you need about 120hp, if you use a 150hp engine because that is the closest available ≥120hp then the car will go 210km/h. It’s the same with printing.
- Outlet temperature
- Fremdgegendruck is the pressure at the end of the outlet pipeline. If it is connected to the atmopshere. It will be 1 atm. Gegendruck (Backpressure) is the pressure at the outlet of the valve. Built up back pressure is pressure generated as a result of fluid flowing through PSV in open mode. There are static and dynamic back pressure. The static pressure comes from the height of the flare and the dynamic from the flow rate in the pipeline.
- Ansprechdruck (response pressure) is the pressure before the safety valve, while the Einstelldruck (set pressure) is the difference between Ansprechdruck and Fremdgegendruck. The Eigengegendruck depends on the stream. The set pressure depends on the temperature. The more the temperature, the higher the compression of the feather should be more to result in the same force.
- Inlet pipeline: the pressure loss in the inlet pipeline including bends and fittings should not be higher than 3% of set pressure for a stabile operation according to the standard API 520. This 3% can be lower for some special cases, which should be analysed in the labratory.
- Outlet pipeline: the permissible pressure loss of the outlet pipeline should be specified from the manufacturer. Regarding the allowable pressure drop,the outlet pipeline can be designed. The mach number should be checked in the outline to verify critical flows. Fremdgegendruck is the pressure of the flare pipeline and blowdown pipeline and Eigengegendruck is the pressure loss due to the stream. If the total pressure loss, Fremdgegendruck+Eigengegendruck, would be too high, there would be a need to use compensators (such as Faltenbalg)
Faltenbalg is used to prevent the emission of gas into atmosphere. It is for the sealing of the valve.
Normally, there is a filter prior to the flare system to prevent the blocking of a pipeline.
The diameter of inlet and outline pipeline should be higher than the size of valve.
Disposal system API521, Chapter 5:
to conduct the relieved fluid to a location where it can be safely discharged:
- Flash point, flammable limits and ignition temperature (referring to NFPA HAZ01)
- Temperature:
- Nonvolatile liquids and volatile liquids could be discharged into a system containing the pressure
- Hot liquids and vapours may be cooled and condensed
- Low temperature
3. Basis for PRD Laterals and Disposal System Headers based on device: Tail Pipes , PRV-Rated Capacity, are piping directly downstream of the PSV., while Lateral is typically a subheader that collects discharges from various PSVs and routes them into the main flare header.
4. Piping
- Design of disposal based on ASME B31.3
- Installation details and criteria API520–2
- Line Sizing: vapor would be considered as a compressible fluid. It would be easy to start from the outlet, where the pressure known, and working back to through the system to verify acceptable backpressure at each PRD
I. Isothermal pressure drop calculation
II. Adiabatic pressure drop calculation
Safety related valve should be checked every two years. They can not be changed regurarly.
- The gas detection could be used on the floor or higher. It depends on the components. H2, ethen, CO are lighter than air, while more components such as H2S (colorless with odoer of rotten eggs) are heavier. CO concentration (colorless, odorless, and tasteless) must not be more than 30 ppm.
To prevent the contact between air and combustile components, N2-Blanket should be used.
Lower Explosion Limit, LEL (Untere Explosionsgrenze, UEG):
The Lower Explosive Limit (LEL) is the lowest concentration of a gas or vapour that will burn in air. The Lower Explosive Limit (LEL) varies from gas to gas, but for most flammable gases it is less than 5% by volume.
Emergency expansion (Notentspannung):
In order to flush a reactor free of carbon hydrates, it is highly recommended to pressurize the column and expand it instead of flushing it with a continous stream. A continous flow of nitrogen is restricted and can not cover the dead points of the reactor. The higher pressure difference can not be the reason for the quicker expansion since there is a restriction orifice prior to the flare. If the critical pressure difference is achieved, then the higher pressure difference will not work.
